
Health inequities have a very real and often deadly cost to human life, evidenced by the declining life expectancy of adults in the United States. These inequities also place an economic burden on communities and states across the country.
We analyzed the cost of racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic health inequities across the U.S. economy, quantifying how these disparities are just as deadly to the economy as they are to human life and wellbeing. It is imperative that policymakers at all levels continue investing resources in order to eliminate health inequities in the U.S. in order to save and improve lives and promote quality health for everyone.
The analyses found that the costs of racial, ethnic health, and socioeconomic inequities are unacceptably high and that policymakers on all levels must continue investing resources to eliminate these disparities in the US.











Click on a state to view its data.
Figure 1 from the Racial and Ethnic Health Report.
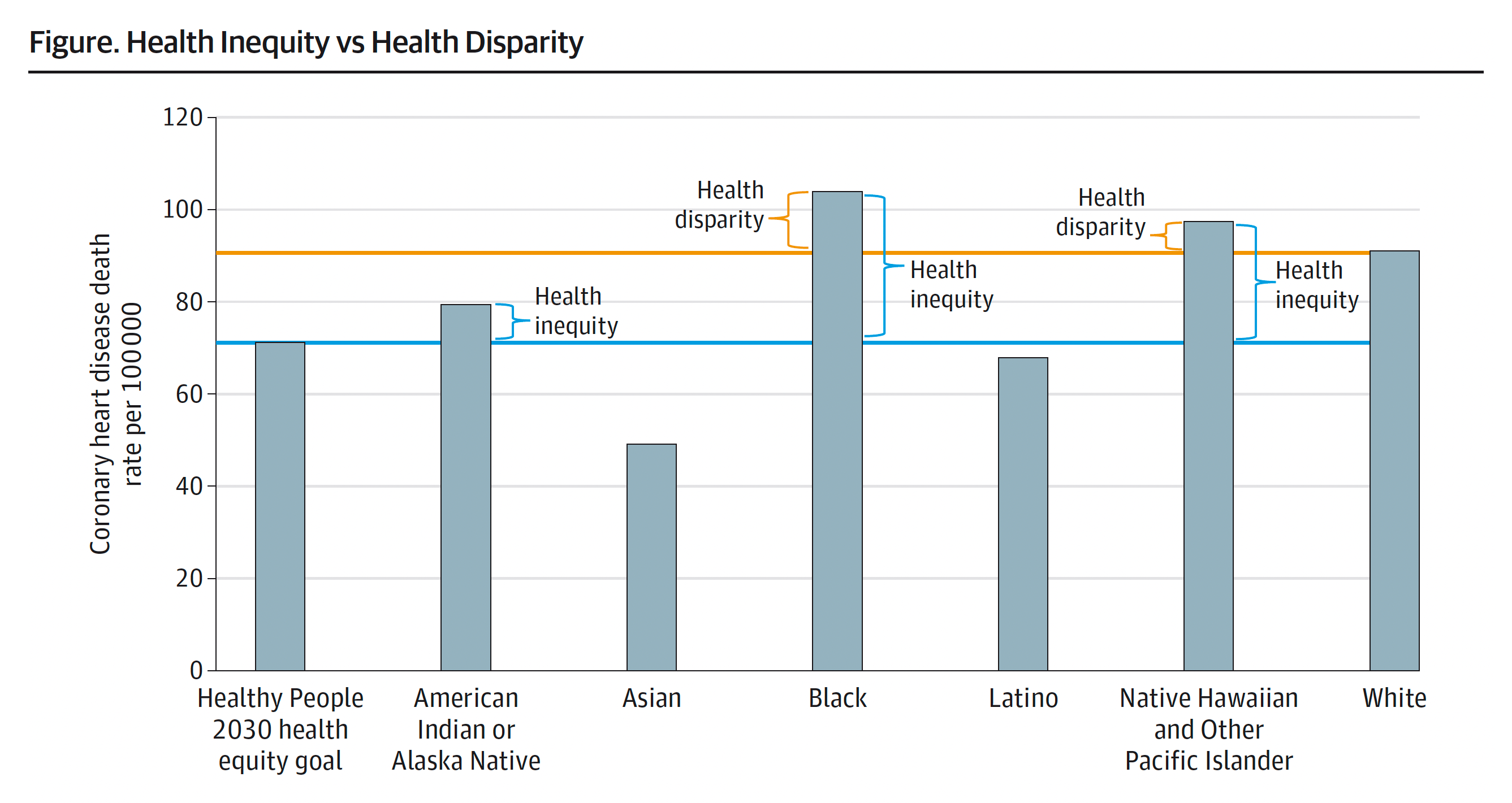
Table 1 from the Racial and Ethnic Health Report.
- Abbreviations: BRFSS, Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System; MEPS, Medical Expenditure Panel Survey; NVSS, National Vital Statistics System.
- Native Hawaiian and Other Pacific Islander samples in the MEPS for age-sex cohorts were too small to compute estimates for medical care spending and labor market productivity.
- Because the study primarily focuses on the burden of health inequities for racial and ethnic minorities, state-level estimates were not computed for the White population using the BRFSS.
|
|
Cost, $ in billions |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Outcome |
American Indian or Alaska Native |
Asian |
Black |
Latino |
Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander |
Total health inequities for non-White populations |
White |
Total |
|
MEPS and National NVSS Estimates |
||||||||
|
Excess medical care costs |
2.8 |
4.9 |
42.0 |
25.4 |
|
75.1 |
183.3 |
258.4 |
|
Lost labor market productivity |
4.7 |
0.9 |
31.5 |
22.0 |
|
59.1 |
90.0 |
149.1 |
|
Excess premature deaths |
20.0 |
0.0 |
238.0 |
9.4 |
19.5 |
286.9 |
335.4 |
622.3 |
|
Total |
27.5 |
5.8 |
311.5 |
56.8 |
19.5 |
421.1 |
608.7 |
1029.8 |
|
BRFSS and State NVSS Estimates |
||||||||
|
Excess medical care costs |
3.5 |
4.6 |
36.8 |
31.3 |
0.6 |
76.8 |
|
|
|
Lost labor market productivity |
3.3 |
3.6 |
33.2 |
40.3 |
0.6 |
81.0 |
|
|
|
Excess premature deaths |
19.5 |
0.2 |
239.6 |
22.6 |
11.1 |
293.0 |
|
|
|
Total |
26.3 |
8.4 |
309.6 |
94.2 |
12.3 |
450.8 |
|
|
Table 2 from the Racial and Ethnic Health Report. The bar graph is a visual representation of each number for purposes of comparison.
To compute excess medical care costs and lost labor market productivity, the authors computed states level estimates for 50 states and the District of Columbia (DC). State level prevalence rates for each race and ethnic group were computed using data from the 2016-2019 BRFSS. These rates were used to simulate medical care costs and labor market outcomes adjusting for age, gender, race, marital status, insurance status, education, family income, health status, health conditions and census regions of the country). Excess premature death costs were computed for each state and DC using state level data from National Vital Statistic System. GDP by states are published by The Bureau of Economic Analysis.
- Abbreviations: BRFSS, Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System; MEPS, Medical Expenditure Panel Survey; NVSS, National Vital Statistics System.
- Per-capita costs for each racial and ethnic group were computed by dividing the total economic loss for that group by the total population of each racial and ethnic group within their respective state.
- State-level estimates for the White population were not computed because the study focused on burden of health inequities for racial and ethnic minority populations. The national per-capita estimate for the White population based on the MEPS estimate was $3098.
| State | Total |
|---|---|
| AL | 13741.2 |
| AK | 2253.9 |
| AZ | 7867.7 |
| AR | 4652.6 |
| CA | 39502.5 |
| CO | 4131.4 |
| CT | 2330.3 |
| DE | 1839.3 |
| DC | 3487.4 |
| FL | 27346.5 |
| GA | 21156.0 |
| HI | 4457.5 |
| ID | 1407.0 |
| IL | 29253.8 |
| IN | 6849.7 |
| IA | 1533.4 |
| KS | 3541.8 |
| KY | 4097.8 |
| LA | 15308.8 |
| ME | 280.6 |
| MD | 14412.7 |
| MA | 3637.0 |
| MI | 16074.9 |
| MN | 4620.2 |
| MS | 10290.0 |
| MO | 8673.9 |
| MT | 1367.2 |
| NE | 1483.7 |
| NV | 8748.2 |
| NH | 284.3 |
| NJ | 10287.3 |
| NM | 5933.5 |
| NY | 18750.5 |
| NC | 19817.3 |
| ND | 767.1 |
| OH | 14868.9 |
| OK | 7677.2 |
| OR | 1745.6 |
| PA | 14723.2 |
| RI | 1187.0 |
| SC | 12140.9 |
| SD | 1587.0 |
| TN | 11211.9 |
| TX | 40606.2 |
| UT | 2565.3 |
| VT | 47.4 |
| VA | 11606.4 |
| WA | 5161.2 |
| WV | 403.4 |
| WI | 4568.6 |
| WY | 229.5 |
| State | American Indian or Alaska Native |
|---|---|
| AL | 9977 |
| AK | 17057 |
| AZ | 13247 |
| AR | 8550 |
| CA | 11240 |
| CO | 10274 |
| CT | 3769 |
| DE | 5585 |
| DC | 7480 |
| FL | 11504 |
| GA | 2176 |
| HI | 2428 |
| ID | 10335 |
| IL | 8295 |
| IN | 3586 |
| IA | 11168 |
| KS | 16676 |
| KY | 14348 |
| LA | 5651 |
| ME | 7232 |
| MD | 6228 |
| MA | 8850 |
| MI | 16615 |
| MN | 22096 |
| MS | 15517 |
| MO | 4577 |
| MT | 17314 |
| NE | 12245 |
| NV | 9571 |
| NH | 18509 |
| NJ | 3311 |
| NM | 12899 |
| NY | 3141 |
| NC | 10051 |
| ND | 15406 |
| OH | 6922 |
| OK | 12593 |
| OR | 10225 |
| PA | 13243 |
| RI | 9632 |
| SC | 4724 |
| SD | 20275 |
| TN | 13220 |
| TX | 6108 |
| UT | 9824 |
| VT | 9209 |
| VA | 2328 |
| WA | 17976 |
| WV | 10054 |
| WI | 10802 |
| WY | 10209 |
| State | Asian |
|---|---|
| AL | 71 |
| AK | 164 |
| AZ | 398 |
| AR | 16 |
| CA | 634 |
| CO | 219 |
| CT | 353 |
| DE | 169 |
| DC | 197 |
| FL | 263 |
| GA | 325 |
| HI | 782 |
| ID | 71 |
| IL | 475 |
| IN | 192 |
| IA | 59 |
| KS | 263 |
| KY | 28 |
| LA | 53 |
| ME | 147 |
| MD | 649 |
| MA | 187 |
| MI | 156 |
| MN | 314 |
| MS | 74 |
| MO | 269 |
| MT | 245 |
| NE | 119 |
| NV | 641 |
| NH | 24 |
| NJ | 777 |
| NM | 171 |
| NY | 819 |
| NC | 300 |
| ND | 174 |
| OH | 101 |
| OK | 155 |
| OR | 346 |
| PA | 283 |
| RI | 148 |
| SC | 105 |
| SD | 29 |
| TN | 116 |
| TX | 130 |
| UT | 110 |
| VT | 143 |
| VA | 445 |
| WA | 511 |
| WV | 653 |
| WI | 160 |
| WY | 148 |
| State | Black |
|---|---|
| AL | 10254 |
| AK | 6490 |
| AZ | 5888 |
| AR | 9387 |
| CA | 7801 |
| CO | 6042 |
| CT | 5012 |
| DE | 7158 |
| DC | 10912 |
| FL | 6459 |
| GA | 6334 |
| HI | 1827 |
| ID | 2058 |
| IL | 9836 |
| IN | 10185 |
| IA | 9058 |
| KS | 9650 |
| KY | 9968 |
| LA | 9965 |
| ME | 814 |
| MD | 7190 |
| MA | 3770 |
| MI | 10202 |
| MN | 5579 |
| MS | 8801 |
| MO | 11790 |
| MT | 648 |
| NE | 7793 |
| NV | 9613 |
| NH | 816 |
| NJ | 7068 |
| NM | 5808 |
| NY | 4340 |
| NC | 7486 |
| ND | 411 |
| OH | 10022 |
| OK | 11100 |
| OR | 8321 |
| PA | 8940 |
| RI | 4198 |
| SC | 8929 |
| SD | 184 |
| TN | 9494 |
| TX | 6987 |
| UT | 3653 |
| VT | 362 |
| VA | 6575 |
| WA | 7205 |
| WV | 4108 |
| WI | 10636 |
| WY | 175 |
| State | Latino |
|---|---|
| AL | 1494 |
| AK | 6461 |
| AZ | 1048 |
| AR | 857 |
| CA | 828 |
| CO | 2018 |
| CT | 855 |
| DE | 4086 |
| DC | 419 |
| FL | 1133 |
| GA | 687 |
| HI | 7073 |
| ID | 5621 |
| IL | 5136 |
| IN | 1268 |
| IA | 2526 |
| KS | 4803 |
| KY | 2681 |
| LA | 1222 |
| ME | 10095 |
| MD | 2472 |
| MA | 2177 |
| MI | 2761 |
| MN | 5012 |
| MS | 2145 |
| MO | 1063 |
| MT | 6365 |
| NE | 3082 |
| NV | 6725 |
| NH | 4819 |
| NJ | 914 |
| NM | 3300 |
| NY | 1326 |
| NC | 2619 |
| ND | 6070 |
| OH | 1295 |
| OK | 2452 |
| OR | 989 |
| PA | 2535 |
| RI | 5696 |
| SC | 680 |
| SD | 4133 |
| TN | 1365 |
| TX | 1501 |
| UT | 4723 |
| VT | 1709 |
| VA | 1126 |
| WA | 761 |
| WV | 3147 |
| WI | 612 |
| WY | 1754 |
| State | Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander |
|---|---|
| AL | 1358 |
| AK | 604 |
| AZ | 20487 |
| AR | 2555 |
| CA | 35476 |
| CO | 12705 |
| CT | 3195 |
| DE | 11126 |
| DC | 443 |
| FL | 36384 |
| GA | 13201 |
| HI | 24017 |
| ID | 9728 |
| IL | 2710 |
| IN | 954 |
| IA | 1877 |
| KS | 3292 |
| KY | 25084 |
| LA | 6839 |
| ME | 6020 |
| MD | 1805 |
| MA | 3106 |
| MI | 578 |
| MN | 2410 |
| MS | 17241 |
| MO | 7056 |
| MT | 9739 |
| NE | 3119 |
| NV | 20712 |
| NH | 6078 |
| NJ | 1187 |
| NM | 3914 |
| NY | 33195 |
| NC | 17124 |
| ND | 590 |
| OH | 1151 |
| OK | 1032 |
| OR | 13064 |
| PA | 1017 |
| RI | 444 |
| SC | 1595 |
| SD | 1631 |
| TN | 549 |
| TX | 37993 |
| UT | 6968 |
| VT | 998 |
| VA | 16909 |
| WA | 21175 |
| WV | 5474 |
| WI | 512 |
| WY | 1348 |
| Location | American Indian or Alaska Native | Asian | Black | Latino | Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AL | 9977 | 71 | 10254 | 1494 | 1358 |
| AK | 17057 | 164 | 6490 | 6461 | 604 |
| AZ | 13247 | 398 | 5888 | 1048 | 20487 |
| AR | 8550 | 16 | 9387 | 857 | 2555 |
| CA | 11240 | 634 | 7801 | 828 | 35476 |
| CO | 10274 | 219 | 6042 | 2018 | 12705 |
| CT | 3769 | 353 | 5012 | 855 | 3195 |
| DE | 5585 | 169 | 7158 | 4086 | 11126 |
| DC | 7480 | 197 | 10912 | 419 | 443 |
| FL | 11504 | 263 | 6459 | 1133 | 36384 |
| GA | 2176 | 325 | 6334 | 687 | 13201 |
| HI | 2428 | 782 | 1827 | 7073 | 24017 |
| ID | 10335 | 71 | 2058 | 5621 | 9728 |
| IL | 8295 | 475 | 9836 | 5136 | 2710 |
| IN | 3586 | 192 | 10185 | 1268 | 954 |
| IA | 11168 | 59 | 9058 | 2526 | 1877 |
| KS | 16676 | 263 | 9650 | 4803 | 3292 |
| KY | 14348 | 28 | 9968 | 2681 | 25084 |
| LA | 5651 | 53 | 9965 | 1222 | 6839 |
| ME | 7232 | 147 | 814 | 10095 | 6020 |
| MD | 6228 | 649 | 7190 | 2472 | 1805 |
| MA | 8850 | 187 | 3770 | 2177 | 3106 |
| MI | 16615 | 156 | 10202 | 2761 | 578 |
| MN | 22096 | 314 | 5579 | 5012 | 2410 |
| MS | 15517 | 74 | 8801 | 2145 | 17241 |
| MO | 4577 | 269 | 11790 | 1063 | 7056 |
| MT | 17314 | 245 | 648 | 6365 | 9739 |
| NE | 12245 | 119 | 7793 | 3082 | 3119 |
| NV | 9571 | 641 | 9613 | 6725 | 20712 |
| NH | 18509 | 24 | 816 | 4819 | 6078 |
| NJ | 3311 | 777 | 7068 | 914 | 1187 |
| NM | 12899 | 171 | 5808 | 3300 | 3914 |
| NY | 3141 | 819 | 4340 | 1326 | 33195 |
| NC | 10051 | 300 | 7486 | 2619 | 17124 |
| ND | 15406 | 174 | 411 | 6070 | 590 |
| OH | 6922 | 101 | 10022 | 1295 | 1151 |
| OK | 12593 | 155 | 11100 | 2452 | 1032 |
| OR | 10225 | 346 | 8321 | 989 | 13064 |
| PA | 13243 | 283 | 8940 | 2535 | 1017 |
| RI | 9632 | 148 | 4198 | 5696 | 444 |
| SC | 4724 | 105 | 8929 | 680 | 1595 |
| SD | 20275 | 29 | 184 | 4133 | 1631 |
| TN | 13220 | 116 | 9494 | 1365 | 549 |
| TX | 6108 | 130 | 6987 | 1501 | 37993 |
| UT | 9824 | 110 | 3653 | 4723 | 6968 |
| VT | 9209 | 143 | 362 | 1709 | 998 |
| VA | 2328 | 445 | 6575 | 1126 | 16909 |
| WA | 17976 | 511 | 7205 | 761 | 21175 |
| WV | 10054 | 653 | 4108 | 3147 | 5474 |
| WI | 10802 | 160 | 10636 | 612 | 512 |
| WY | 10209 | 148 | 175 | 1754 | 1348 |
| US (overall) | 12351 | 487 | 7797 | 1643 | 23225 |
| Mean (SD) across states | 10,281 (4,930) | 262 (215) | 6,614 (3,390) | 2,856 (2,183) | 8,976 (10,551) |
Table 3 from the Socioeconomic Health Report.
- Abbreviations: BRFSS, Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System; MEPS, Medical Expenditure Panel Survey; NVSS, National Vital Statistics System.
- State-level estimates for adults with 4-year college or more were not computed because the study focuses on burden of health inequities for adults with lower educational attainment.
|
|
Cost, $ in billions |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Outcome |
Less than high school |
High school / GED |
Some College |
Total health inequities for adults with <4-year college degree |
4-year college degree or more |
Total |
|
MEPS and national NVSS estimates |
||||||
|
Excess medical care costs |
37.4 |
62.1 |
48.3 |
147.8 |
27.9 |
175.7 |
|
Lost labor market productivity |
30.4 |
67.4 |
59.0 |
156.8 |
7.4 |
164.2 |
|
Premature death |
175.9 |
455.4 |
4.5 |
635.8 |
0.0 |
635.8 |
|
Total |
243.7 |
584.9 |
111.8 |
940.4 |
35.3 |
975.7 |
|
BRFSS and state NVSS estimates |
||||||
|
Excess medical care costs |
44.5 |
64.1 |
46.3 |
154.9 |
|
|
|
Lost labor market productivity |
32.4 |
72.3 |
69.3 |
154.9 |
|
|
|
Premature death |
178.9 |
457.0 |
12.9 |
648.7 |
|
|
|
Total |
255.8 |
593.4 |
128.5 |
977.7 |
|
|
Table 4 from the Socioeconomic Health Report. The bar graph is a visual representation of each number for purposes of comparison.
- Per-capita costs were computed by dividing populations of each education group for adults older than 25 years.
- State-level estimates for adults with 4-year college or more were not computed because the study focuses on burden of health inequities for adults with lower educational attainment. The US per-capita estimate for adults with a 4-year college degree was $514.
| State | Total Economic Burden |
|---|---|
| AL | 28431 |
| AK | 2278 |
| AZ | 16484 |
| AR | 13210 |
| CA | 59463 |
| CO | 11203 |
| CT | 7380 |
| DE | 3523 |
| DC | 2710 |
| FL | 57230 |
| GA | 32384 |
| HI | 2727 |
| ID | 3974 |
| IL | 3974 |
| IN | 24224 |
| IA | 8749 |
| KS | 8264 |
| KY | 26132 |
| LA | 23145 |
| ME | 4621 |
| MD | 19037 |
| MA | 18343 |
| MI | 43710 |
| MN | 10209 |
| MS | 15561 |
| MO | 23704 |
| MT | 2689 |
| NE | 5220 |
| NV | 7864 |
| NH | 4443 |
| NJ | 20577 |
| NM | 7930 |
| NY | 36411 |
| NC | 48508 |
| ND | 1625 |
| OH | 47793 |
| OK | 16800 |
| OR | 10551 |
| PA | 43518 |
| RI | 2616 |
| SC | 42871 |
| SD | 2488 |
| TN | 36302 |
| TX | 71127 |
| UT | 5295 |
| VT | 1824 |
| VA | 22055 |
| WA | 19095 |
| WV | 6154 |
| WI | 14068 |
| WY | 1655 |
| State | Less than High School |
|---|---|
| AL | 19194 |
| AK | 14804 |
| AZ | 7373 |
| AR | 15356 |
| CA | 3152 |
| CO | 6623 |
| CT | 5421 |
| DE | 10815 |
| DC | 14396 |
| FL | 8507 |
| GA | 11200 |
| HI | 4572 |
| ID | 8524 |
| IL | 7798 |
| IN | 12978 |
| IA | 9106 |
| KS | 8888 |
| KY | 21372 |
| LA | 19291 |
| ME | 14075 |
| MD | 11295 |
| MA | 6833 |
| MI | 20842 |
| MN | 7005 |
| MS | 18415 |
| MO | 16296 |
| MT | 13769 |
| NE | 7395 |
| NV | 4691 |
| NH | 12328 |
| NJ | 4691 |
| NM | 10816 |
| NY | 3631 |
| NC | 15833 |
| ND | 10014 |
| OH | 15706 |
| OK | 14731 |
| OR | 8785 |
| PA | 10217 |
| RI | 8464 |
| SC | 19954 |
| SD | 12145 |
| TN | 19082 |
| TX | 5815 |
| UT | 8100 |
| VT | 15049 |
| VA | 13246 |
| WA | 17037 |
| WV | 11318 |
| WI | 8827 |
| WY | 12029 |
| State | High School / GED |
|---|---|
| AL | 16535 |
| AK | 10837 |
| AZ | 7945 |
| AR | 11448 |
| CA | 6280 |
| CO | 9653 |
| CT | 7241 |
| DE | 11418 |
| DC | 22430 |
| FL | 8069 |
| GA | 9355 |
| HI | 7085 |
| ID | 7586 |
| IL | 9352 |
| IN | 10643 |
| IA | 9145 |
| KS | 10306 |
| KY | 14738 |
| LA | 11145 |
| ME | 9423 |
| MD | 11857 |
| MA | 11836 |
| MI | 13225 |
| MN | 7426 |
| MS | 12321 |
| MO | 11165 |
| MT | 7683 |
| NE | 11884 |
| NV | 9662 |
| NH | 10819 |
| NJ | 8868 |
| NM | 11066 |
| NY | 6614 |
| NC | 14467 |
| ND | 8108 |
| OH | 11733 |
| OK | 11846 |
| OR | 8632 |
| PA | 9621 |
| RI | 7336 |
| SC | 25555 |
| SD | 8817 |
| TN | 14553 |
| TX | 10452 |
| UT | 6661 |
| VT | 7939 |
| VA | 8597 |
| WA | 7283 |
| WV | 6201 |
| WI | 7263 |
| WY | 8784 |
| State | Some College |
|---|---|
| AL | 2391 |
| AK | 1944 |
| AZ | 1958 |
| AR | 1866 |
| CA | 1478 |
| CO | 1171 |
| CT | 1993 |
| DE | 2362 |
| DC | 2532 |
| FL | 1794 |
| GA | 2335 |
| HI | 1311 |
| ID | 1993 |
| IL | 1072 |
| IN | 1520 |
| IA | 1956 |
| KS | 2672 |
| KY | 2677 |
| LA | 2588 |
| ME | 2467 |
| MD | 2136 |
| MA | 1423 |
| MI | 1909 |
| MN | 1162 |
| MS | 3874 |
| MO | 2041 |
| MT | 1582 |
| NE | 1214 |
| NV | 1625 |
| NH | 2739 |
| NJ | 1800 |
| NM | 3587 |
| NY | 1846 |
| NC | 4223 |
| ND | 1131 |
| OH | 1839 |
| OK | 3305 |
| OR | 2499 |
| PA | 1997 |
| RI | 1791 |
| SC | 8374 |
| SD | 2124 |
| TN | 2845 |
| TX | 1337 |
| UT | 2228 |
| VT | 2572 |
| VA | 1287 |
| WA | 1993 |
| WV | 2850 |
| WI | 1946 |
| WY | 2309 |
| Cost, $ | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Location | Less than high school | High school / GED | Some college |
| AL | 19194 | 16535 | 2391 |
| AK | 14804 | 10837 | 1944 |
| AZ | 7373 | 7945 | 1958 |
| AR | 15356 | 11448 | 1866 |
| CA | 3152 | 6280 | 1478 |
| CO | 6623 | 9653 | 1171 |
| CT | 5421 | 7241 | 1993 |
| DE | 10815 | 11418 | 2362 |
| DC | 14396 | 22430 | 2532 |
| FL | 8507 | 8069 | 1794 |
| GA | 11200 | 9355 | 2335 |
| HI | 4572 | 7085 | 1311 |
| ID | 8524 | 7586 | 1993 |
| IL | 7798 | 9352 | 1072 |
| IN | 12978 | 10643 | 1520 |
| IA | 9106 | 9145 | 1956 |
| KS | 8888 | 10306 | 2672 |
| KY | 21372 | 14738 | 2677 |
| LA | 19291 | 11145 | 2588 |
| ME | 14075 | 9423 | 2467 |
| MD | 11295 | 11857 | 2136 |
| MA | 6833 | 11836 | 1423 |
| MI | 20842 | 13225 | 1909 |
| MN | 7005 | 7426 | 1162 |
| MS | 18415 | 12321 | 3874 |
| MO | 16296 | 11165 | 2041 |
| MT | 13769 | 7683 | 1582 |
| NE | 7395 | 11884 | 1214 |
| NV | 4691 | 9662 | 1625 |
| NH | 12328 | 10819 | 2739 |
| NJ | 4691 | 8868 | 1800 |
| NM | 10816 | 11066 | 3587 |
| NY | 3631 | 6614 | 1846 |
| NC | 15833 | 14467 | 4223 |
| ND | 10014 | 8108 | 1131 |
| OH | 15706 | 11733 | 1839 |
| OK | 14731 | 11846 | 3305 |
| OR | 8785 | 8632 | 2499 |
| PA | 10217 | 9621 | 1997 |
| RI | 8464 | 7336 | 1791 |
| SC | 19954 | 25555 | 8374 |
| SD | 12145 | 8817 | 2124 |
| TN | 19082 | 14553 | 2845 |
| TX | 5815 | 10452 | 1337 |
| UT | 8100 | 6661 | 2228 |
| VT | 15049 | 7939 | 2572 |
| VA | 13246 | 8597 | 1287 |
| WA | 17037 | 7283 | 1993 |
| WV | 11318 | 6201 | 2850 |
| WI | 8827 | 7263 | 1946 |
| WY | 12029 | 8784 | 2309 |
| US (overall) | 9467 | 9982 | 2028 |
| Mean (SD) across states | 11,525 (4,843) | 20,371 (3,363) | 2,229 (1,113) |
Table 5 compares data from both the Racial and Ethnic Health Report and the Socioeconomic Health Report.
- The “Racial and ethnic health inequities” totals do not compute state-level estimates for the White population and adults with 4-year college or more because the study focuses on burden of health inequities for disadvantaged populations.
- The “Education-related health inequities” fields are divided by the 2018 gross domestic product for each states and the nation, which are published by The Bureau of Economic Analysis.
| Racial and ethnic health inequities | Education-related health inequities | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location | Total, $ in million | Share of gross domestic product, % | Total, $ in million | Share of gross domestic product, % |
| AL | 13741.2 | 6.12 | 28431 | 12.66 |
| AK | 2253.9 | 4.11 | 2278 | 4.15 |
| AZ | 7867.7 | 2.35 | 16484 | 4.92 |
| AR | 4652.6 | 3.58 | 13210 | 10.18 |
| CA | 39502.5 | 1.31 | 59463 | 1.97 |
| CO | 4131.4 | 1.10 | 11203 | 2.97 |
| CT | 2330.3 | 0.83 | 7380 | 2.64 |
| DE | 1839.3 | 2.40 | 3523 | 4.60 |
| DC | 3487.4 | 2.45 | 2710 | 1.90 |
| FL | 27346.5 | 2.58 | 57230 | 5.40 |
| GA | 21156.0 | 3.52 | 32384 | 5.38 |
| HI | 4457.5 | 4.77 | 2727 | 2.92 |
| ID | 1407.0 | 1.79 | 3974 | 5.05 |
| IL | 29253.8 | 3.32 | 3974 | 5.05 |
| IN | 6849.7 | 1.84 | 24224 | 6.52 |
| IA | 1533.4 | 0.80 | 8749 | 4.54 |
| KS | 3541.8 | 2.09 | 8264 | 4.87 |
| KY | 4097.8 | 1.94 | 26132 | 12.35 |
| LA | 15308.8 | 5.99 | 23145 | 9.06 |
| ME | 280.6 | 0.43 | 4621 | 7.07 |
| MD | 14412.7 | 3.45 | 19037 | 4.56 |
| MA | 3637.0 | 0.63 | 18343 | 3.19 |
| MI | 16074.9 | 2.99 | 43710 | 8.14 |
| MN | 4620.2 | 1.23 | 10209 | 2.72 |
| MS | 10290.0 | 8.89 | 15561 | 13.44 |
| MO | 8673.9 | 2.68 | 23704 | 7.33 |
| MT | 1367.2 | 2.75 | 2689 | 5.42 |
| NE | 1483.7 | 1.19 | 5220 | 4.18 |
| NV | 8748.2 | 5.18 | 7864 | 4.66 |
| NH | 284.3 | 0.33 | 4443 | 5.16 |
| NJ | 10287.3 | 1.62 | 20577 | 3.24 |
| NM | 5933.5 | 5.85 | 7930 | 7.82 |
| NY | 18750.5 | 1.10 | 36411 | 2.14 |
| NC | 19817.3 | 3.44 | 48508 | 8.43 |
| ND | 767.1 | 1.38 | 1625 | 2.92 |
| OH | 14868.9 | 2.16 | 47793 | 6.94 |
| OK | 7677.2 | 3.78 | 16800 | 8.27 |
| OR | 1745.6 | 0.72 | 10551 | 4.34 |
| PA | 14723.2 | 1.83 | 43518 | 5.42 |
| RI | 1187.0 | 1.94 | 2616 | 4.26 |
| SC | 12140.9 | 5.18 | 42871 | 18.29 |
| SD | 1587.0 | 3.02 | 2488 | 4.74 |
| TN | 11211.9 | 3.00 | 36302 | 9.72 |
| TX | 40606.2 | 2.23 | 71127 | 3.91 |
| UT | 2565.3 | 1.42 | 5295 | 2.93 |
| VT | 47.4 | 0.14 | 1824 | 5.34 |
| VA | 11606.4 | 2.13 | 22055 | 4.05 |
| WA | 5161.2 | 0.90 | 19095 | 3.31 |
| WV | 403.4 | 0.51 | 6154 | 7.77 |
| WI | 4568.6 | 1.33 | 14068 | 4.11 |
| WY | 229.5 | 0.58 | 1655 | 4.15 |
| Total | 12187.6 | 2086514.0 | 977675 | 4.69 |
Racial and Ethnic Health Report
What is the cost to the US economy of socioeconomic health inequities?
The economic burden in this category ranges from $421-$451 billion. Most of these inequities exist due to the exposure to economic, social, structural, and environmental risks and their healthcare access. The report measures the sum of excess medical care costs, lost labor market productivity, and excess premature death (before age 78) costs by race and ethnicity compared to health equity goals.
Socioeconomic Health Report
What is the cost to the US economy of socioeconomic health inequities?
The Socioeconomic Health Report found that the costs of socioeconomic health inequities are $940-$978 billion. Most of these costs were attributed to adults with a high school diploma. However, a disproportionate share of the expenses was attributed to adults with less than a high school education. The study was conducted to estimate the economic burden of socioeconomic health inequities in the US. The measures included excess medical care costs, lost labor market productivity, and excess premature death costs.
About the Tulane Institute for Innovation in Health Equity
The Tulane Institute for Innovations in Health Equity serves as a forum to promote scholarship advancing the reduction and elimination of preventable differences in the burden of disease. Health inequities impact a wide variety of demographic groups in not just the United States, but all over the world. The quest for health equity addresses both historical and contemporary injustices based on race, ethnicity, socio-economic status, gender, sexuality, disability status, and more.
The institute is comprised of centers, research projects, and individual researchers who explore unjust patterns in the distribution of disease that are avoidable and preventable. We work to enhance human health through engagement of disadvantaged communities and populations and to serve as a resource for education and training.
If you are a member of the media looking for information about these reports, please visit our Media Inquiries page.
